Other Various Recommended Implementation Patterns
Introduce recommended implementation patterns considering operation on AWS Lambda, regardless of application type.
Recommended Configuration When Using AWS SDK
Implement and deploy AWS SDK (boto3) wrapper classes in the aws directory and use them as modules.
The benefits are as follows:
- Improved reusability
- Serverless applications especially have many AWS service calls
- Improved test convenience and maintainability
- Ease of mocking
- Minimize impact scope from AWS SDK version upgrades and specification changes
- Improved code readability
Not only for AWS SDK, but when using external API calls or libraries, you can enjoy the above benefits by using a similar configuration.
Wrapper Class Example
For example, the following is an implementation example of a wrapper class for the part that accesses S3.
import boto3, os
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION = os.getenv('AWS_DEFAULT_REGION', 'ap-northeast-1')
class S3Client:
def __init__(self):
self.s3_client = boto3.client(
service_name='s3',
region_name=AWS_DEFAULT_REGION,
endpoint_url=os.getenv('S3_ENDPOINT_URL')
)
def get_object_as_string(self, **kwargs):
bucket = kwargs['bucket']
key = kwargs['key']
response = self.s3_client.get_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=key)
utf8_decoded_string = response['Body'].read().decode('utf-8')
return utf8_decoded_string
def upload(self, **kwargs):
file_path = kwargs['file_path']
bucket = kwargs['bucket']
key = kwargs['key']
self.s3_client.upload_file(file_path, bucket, key)
def download(self, **kwargs):
file_path = kwargs['file_path']
bucket = kwargs['bucket']
key = kwargs['key']
self.s3_client.download_file(bucket, key, file_path)
Logger
To output JSON structured logs recommended by this catalog, we explain the log output method using Logger from Powertools for AWS Lambda (Python).
- Powertools for AWS Lambda (Python) - Logger
Usage
Instantiate and use as follows. You can also add or remove items according to your needs. Please perform initialization and configuration (context reflection) at the start of the Lambda entry point or by separately defining a logger class.
src/sample_api/index.py
@logger.inject_lambda_context(correlation_id_path=correlation_paths.API_GATEWAY_REST, clear_state=True)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# For Logger customization and key addition, please refer to the following.
# You can also use customization by creating a separate Logger wrapper class and performing various settings.
# https://docs.powertools.aws.dev/lambda/python/latest/core/logger/#append_keys-method
additional_log_attributes = {
"process": "%(process)d",
"processName": "%(processName)s"
}
# Add arbitrary items
logger.append_keys(**additional_log_attributes)
# Remove arbitrary items
logger.remove_keys(["processName"])
return app.resolve(event, context)
By default, logs like the following are output.
{
"level": "INFO",
"location": "create_news:19",
"message": "Created new news record - {'news_type': 'sports', 'title': 'sample_news_title', 'content': 'sample_news_conten'}",
"timestamp": "2025-04-20 01:51:45,781+0000",
"service": "service_undefined",
"cold_start": true,
"function_name": "tester-function",
"function_memory_size": 256,
"function_arn": "invoked_function_arn",
"function_request_id": "aws_request_id"
}
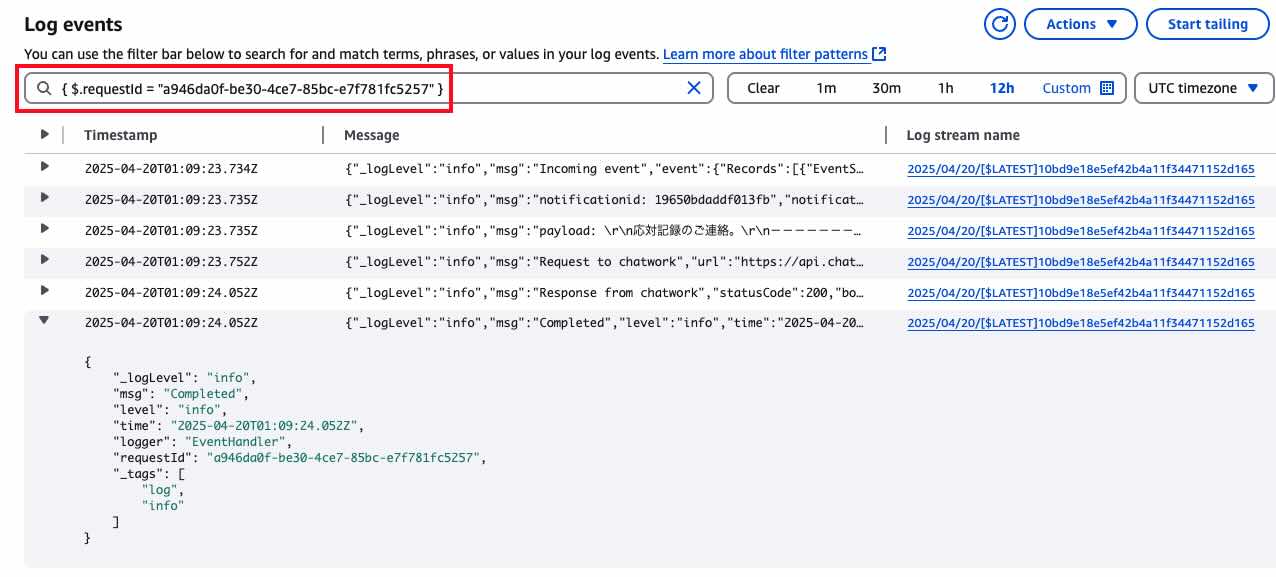
Log Search in CloudWatch Logs
Based on the above format, you can perform log searches in CloudWatch Logs as follows.
# Search by specifying log level
{ $.level = "ERROR" }
# Search by specifying Request ID
{ $.requestId = “xxx” }
When searching in CloudWatch Logs, you get results like the following.