Local Debugging and Testing
This document describes methods for debugging and testing application code by running it in a local development environment.
Overview
Whether AWS Lambda is triggered by Amazon API Gateway (Web API) or Event triggers, the data necessary for processing is contained in the first argument event of the handler function. By creating this Event Payload in advance and running it locally, we can reproduce Lambda behavior.
When integrating with other AWS services such as Amazon DynamoDB or S3 during processing, AWS credentials set in the local environment (access keys in environment variables or ~/.aws/credentials) are used instead of the AWS Lambda execution role. If minio and dynamodb-local are started with docker-compose and their endpoints are specified in the AWS SDK, connections will be made to those containers.
You can check examples of specifying event payloads below.
-
WebAPI Logic
- Handler functions are executed by directly specifying API call request payloads passed from API Gateway (REST API), matching the interface of the API routing library.
.local/sample-api/get-users.ts.local/sample-api/post_users.ts
- Handler functions are executed by directly specifying API call request payloads passed from API Gateway (REST API), matching the interface of the API routing library.
-
Event Triggers
- Handler functions are executed by directly specifying event payloads passed from S3, SNS, SQS, etc.
.local/sample-event/post-s3-event.ts
- Handler functions are executed by directly specifying event payloads passed from S3, SNS, SQS, etc.
Event payload templates can be obtained from the AWS Lambda console. For S3 events, select "S3 Put", and for API Gateway (REST API), select "API Gateway AWS Proxy".
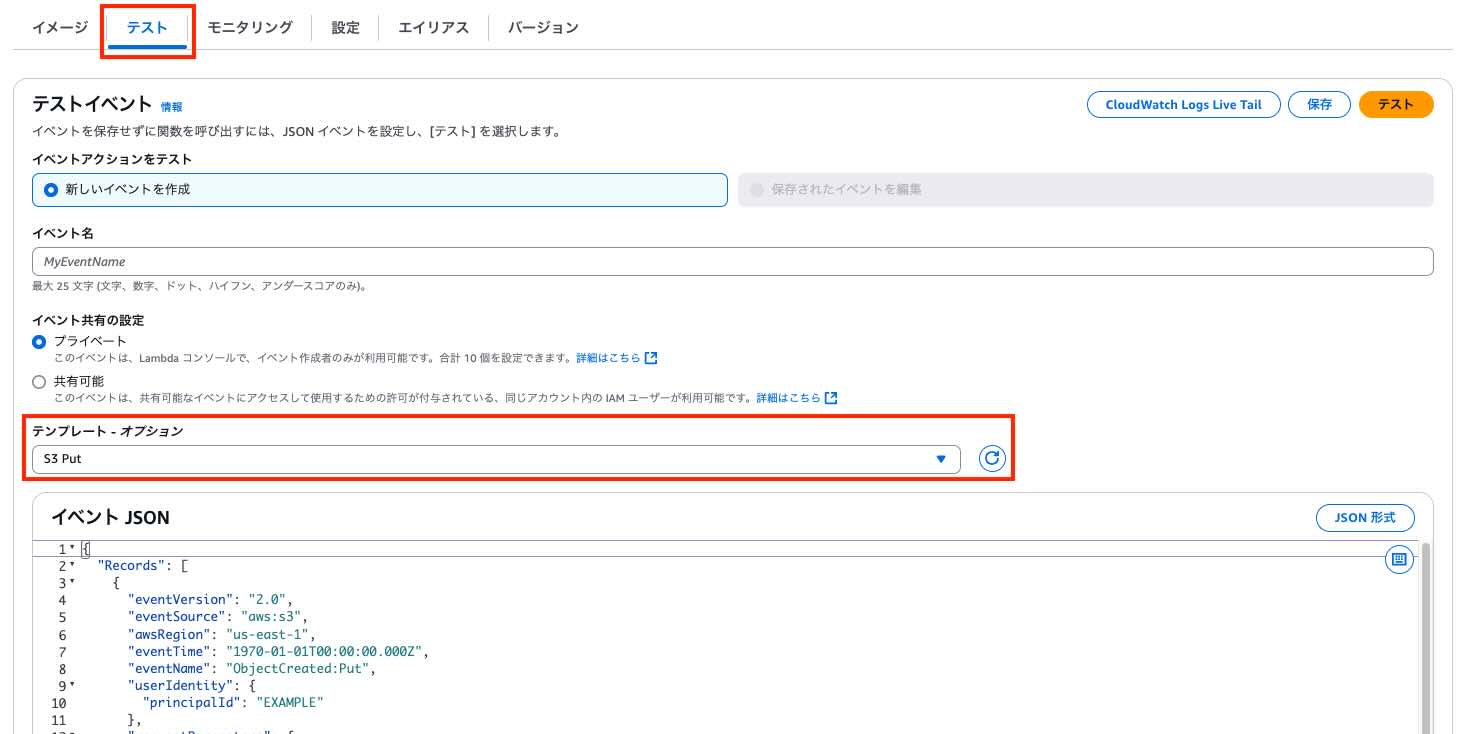
Local Execution Steps
*Note: "Local environment" refers to the EC2 instance environment launched in this catalog.
1. Starting Docker
Local development is performed using dedicated TypeScript scripts, PostgreSQL containers, and MinIO containers (S3-compatible storage). First, let's start these containers defined in docker-compose.yaml.
[ec2-user ~] docker compose up -d
2. DB Setup (Table Creation)
Create databases and tables within the PostgreSQL started in the container. The following TypeScript script automatically creates the database and users table within the container. In addition, a script will be executed to create a test table and populate it with test data in DynamoDB Local.
[ec2-user ~] npx tsx .local/setup-db.ts
[ec2-user ~] npx tsx .local/setup-dynamodb.ts
Alternatively, without using scripts, you can directly use the psql PostgreSQL command-line tool, which is already installed, to manipulate tables within the container. Here we are creating 3 records. When prompted for a password, enter password.
[ec2-user ~]psql -h localhost -U admin -d mydb
mydb=# INSERT INTO users (name, country, age) VALUES
('Alice', 'Japan', 30),
('Bob', 'USA', 25),
('Charlie', 'Germany', 35);
mydb=# exit # This returns you to the normal terminal
3. Local API Execution
GET API
.local/sample-api/get-user.ts is a script that simulates an API for retrieving user data with the GET method. You can debug and verify behavior by modifying the request creation parts within the file.
// Dynamic import after environment variables are set
const { api } = await import('../../src/sample-api')
// Test user ID - change this value to test different cases
const userId = 1
const response = await api.app.request(`/v1/users/${userId}`, {
method: 'GET',
})
const body = await response.json()
[ec2-user ~] npx tsx .local/sample-api/get-user.ts
API Execution Result: {"statusCode": 200, "body": "{\"statusCode\":200,\"body\":{\"name\":\"Alice\",\"country\":\"Japan\",\"age\":30}}", "isBase64Encoded": false, "headers": {"Content-Type": "application/json"}, "cookies": []}
When you actually run the script, a response from the API is returned.
POST API
.local/sample-api/post_user.ts simulates an API for creating users with the POST method. You can develop while manipulating the following Body parameters.
// Dynamic import after environment variables are set
const { api } = await import('../../src/sample-api')
// Test data - change this to test different cases
const userData = {
name: 'Hanako',
country: 'Japan',
age: 25,
}
const response = await api.app.request('/v1/users', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(userData),
})
const body = await response.json()
When you actually execute the script, you can see that the data set in the Body has been created correctly.
[ec2-user ~] npx tsx .local/sample-api/create-user.ts
API Execution Result: {"statusCode": 200, "body": "{\"statusCode\":200,\"body\":{\"message\":\"The data created successfully.\"}}", "isBase64Encoded": false, "headers": {"Content-Type": "application/json"}, "cookies": []}
$ mydb=# SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=4;
id | name | country | age
----+--------+---------+-----
4 | Shigeo | Japan | 30
(1 row)
4. Local S3 Event Execution
For S3 events, we test using MinIO, an S3-compatible storage. Running the following script creates a bucket called test-bucket on MinIO and uploads sample_users.csv.
[ec2-user ~] npx tsx .local/setup-minio.ts
MinIO cannot reproduce direct Lambda triggering. Therefore, .local/sample-event/process-s3-event.ts generates events when Lambda is triggered, enabling local execution. When you run the script, you can see that the contents of sample_users.csv have been created in the DB.
[ec2-user ~] npx tsx .local/sample-event/process-s3-event.ts
mydb=# SELECT * FROM users;
id | name | country | age
----+---------+---------+-----
1 | Alice | Japan | 30
2 | Bob | USA | 25
3 | Charlie | Germany | 35
4 | Shigeo | Japan | 30
5 | Taro | Japan | 30
6 | Alice | USA | 28
7 | Bob | UK | 35
8 | Maria | Germany | 25
9 | Li | China | 32
5. Unit Testing
We also provide sample implementations for unit tests. Using Jest, test code is placed under the tests directory. Unit tests similarly use PostgreSQL and MinIO containers to implement test cases that are considered necessary, such as validation patterns and normal system patterns.
Tests can be executed with the following command.
[ec2-user ~] npm run test
Other Testing Methods
Setting Up a Pseudo Environment in Local Environment
For WebAPI logic, you can use SAM Local (start-api) to start an API server that emulates Amazon API Gateway on localhost.
- SAM Local (SAM CLI)
For Event triggers, you can emulate AWS services in the local environment for testing using the following:
-
Amazon S3
- MinIO (*Available with OSS version)
-
Amazon DynamoDB
- DynamoDB Local (*Official tool distributed by AWS)